Who Can Apply For a Trademark?
In the Trademark Registration form, the person whose name is mentioned as the applicant will be declared as the owner of the trademark once the trademark is successfully registered. Any individual, a company and an LLP can be an applicant and may file the application for the registration of the particular trademark.
How to Register a Trademark ?
Registration of a trademark is done by the registry of the trademarks. When you plan on registering a trademark there are a few steps involved.
Choosing a trademark:
Remember to choose a unique and distinctive mark it will represent your company. The other important point is identifying which class you belong to. Currently, there are 45 classes of goods and services under which the trademark can be registered. Classes 1-34 are for goods and classes 35-45 are for service. You can find the class list here
Mark search:
Once you have chosen your mark it is advisable to conduct a search to check whether your chosen mark is similar to an already registered mark. You can either do this yourself by going to the online website of the Controller general of patents, designs and trademarks. On the website, you can find an option to do a public search. Once click on this option you need to choose your class and search the online database.
The other option is to get legal services, although you will have to pay for it is the safer option.
Overall legal services will cost lesser in case your trademark is objected against. Not only will they do the search they will also help you with the whole process.
Filing application:
There are two options you can take while filing for a trademark.
– File for a trademark under “one” class. Meaning the trademark will be registered only for the specific class that you have chosen.
– The other option is to file for multiple classes or series trademark, or collective trademark. For this, you have to fill in form TM-A. This form allows you to register the trademark beyond one class.
While filling the form make sure not to make any mistakes, this may lead to delays or even rejection of the application. You have to fill in all the details and also add a picture of the trademark with the dimensions of 9 by 5 cm. You may be required to attach five duplicates of the same. The full file must be then submitted with two duplicates when filing.
You can file it online or by yourself or by an agent, whichever is convenient for you. Confirmation of filing will be done immediately if done online, if done physically it may take to 15-20 days.
5. Online Trademark Registration Procedure
Step 1: Surf internet for a brand name that is “wacky-enough”
This is simply a short and best way for any newcomer to get a catchy, trendy, and an interesting brand name. Picking up a brand name that is wacky and quirky is definitely a wise move since most of the generic names would already be in someone’s hands. Moreover, zeroing in on a particular name requires a quick research process to ensure yourself that you are not picking a brand name that is already in use. The best part here is that you can invent or coin some words with a mix of generic words to create a unique brand name for yourself.
Step 2: Preparing a trademark application
The following supporting documents together with the application have to be submitted for online trademark registration:-
– Business Registration Proof: On the basis of your registered business (for eg: sole proprietorship and so on), an identity proof of the company’s directors and an address proof have to be submitted. In case of sole proprietorship business, id proof of the proprietor viz. PAN card, Aadhar card could be submitted. Whereas, in the case of companies, the address proof of the company needs to be submitted.
-Soft copy of the trademark.
– The proof of claim (which is applicable) of the proposed mark can be used in another country.
– Power of attorney to be signed by the applicant.
Step 3: Filing the application of brand name registration
Manual Filing and e-filing are the two different ways for filing the registration. If you choose ‘manual filing’ then you have to personally move and handover your application for the registration to the Registrar Office of Trade Marks situated in the major cities of India like Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Ahmedabad, and Chennai. After that, you have to wait for at least 15 -20 days to receive the receipt of the acknowledgment. But in the case of an e-filing system, you will receive your receipt of acknowledgment instantly on the government website. Once after receiving your acknowledgment, you are eligible to use your Trademark(TM) symbol beside your brand name!
Step 4: Examining the process of the brand name application
Once the application is dispatched, the Registrar will check out whether you have followed certain terms that your brand name complies with, the existing law. Moreover, there should not be any conflict or dispute amongst any existing or pending brands for the registration. This is the reason why we preferred you to choose a quirky brand name!
Step 5: Publication of your brand in the Indian Trade Mark Journals
After the process of examination, the registrar will publish your brand name in the Indian Trade Mark Journal. This is certainly the most important part of the trademark registration and there should not be any opposition within 3 months (i.e. 90 days) or 120 days, in some cases, from the date of publication. Then your brand name is proceeding towards the acceptance.
Step 6: The trademark registration certificate issuance
The Registrar will accept your trademark application if there’s no opposition being raised within the stipulated period of 90 days. Wow! And this will be the happiest moment for you as the Registrar issues the Registration Certificate with the Trademark Registry seal.
Right from the moment you have been issued with your certificate, you can use the registered trademark symbol (®) beside your brand name. Thus, with this blog post, we feel that even a beginner can understand all about creating a brand name and registering it successfully.
6. Status of application
Once you have received the confirmation of the filing of the application you will get an allotment number. You can check the progress of the application online with this allotment number. This will take time, if there is no problem with the filing then you will get to know whether your application is approved or rejected in 18-24 months. If there is a problem then this may take longer.
Files are prioritized according to the filing date, therefore the longer it takes the more priority your application gets. The other perk about filing the application is that even if it hasn’t been approved you can use the TM symbol next to your mark, once you have received your allotment number.
7. Registration
Once your trademark is approved the registry will give you a trademark registration certificate. This will officially confirm that your trademark has been registered and is now protected. The registration will be valid for 10 years from the date of the filing of the application. After this period you can renew the trademark again. Renewal can be done indefinitely.
Please Note: A trademark is only protected and valid in India and does not warrant any international status.
8. Top 8 Things You Need to Know Regarding Trademark Registration
A trademark can be one of your company’s most valuable assets. It is a form of identification and contributes significantly towards building the company’s public image. A trademark is a visual symbol – a word, name, numbers, label, logo, a combination of colors etc. It is a mark of uniqueness and helps the customers identify a particular brand or company.
The Trademark Act, 1999, governs the laws related to trademarks and their registration. The trademarks in India are registered by the Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks, (Office of the Registrar of Trademarks), Ministry of Industry and Commerce, Government of India.
Take a look at the top 8 things you need to know about trademark registration:
A Visual Representation
The types of trademarks you can get registered are quite varied. Here are a few types:-
– Word Marks
– Service Marks
– Logos and Symbols
– Shape of Goods
– Series Marks
– Collective Trademarks
– Certification Mark
– Geographical Indicators
– Pattern Marks
– Sound Marks
– Color Marks
– Three Dimensional Marks
An Intangible Asset
Consider the fact that your business builds a reputed name and turns out a successful brand. A trademark, being a type of intellectual property, brings heaps of benefits to the company. Once a trademark is registered, it becomes an intangible asset that can be traded, franchised, commercially contracted and distributed.
Protection Against Infringement and Other Legal Protection
The owner of a registered trademark can exercise his legal rights in case there is any infringement with regard to the owner’s logo, brand, a slogan that has an active trademark against it. The owner has the right to sue any third party that uses the trademark without the prior permission of the owner of the trademark.
Trademark Search
A trademark search is usually carried out to check if a particular trademark already exists. The search can be conducted through the government’s Indian Trademark Registry database or a third-party service provider website.
Class Selection
The goods and services here are classified into 45 different sectors. Each sector is referred to as a class. Every logo or brand name is to be registered under the appropriate class at the time of application. Out of the 45 different classes, 34 of those classes comprise of product classes, and the remaining 11 are for service.
Voluntary, not Compulsory Registration
The registration of a trademark is done on a voluntary basis. However, if a trademark is registered, it holds concrete evidence that the ownership of the trademark belongs to the person who has taken the effort to register it. All legal decisions will be in favour of the party that had the trademark registered.
Validity
A registered trademark has a period of validity that stretches up to 10 years before it has to be renewed again. However, the renewal process may be initiated only within one year before the expiry of the registered trademark. If one fails to do so, the trademark will be removed. Even on removal, the trademark can be reinstated through what is known as restoration of the trademark in the prescribed form.
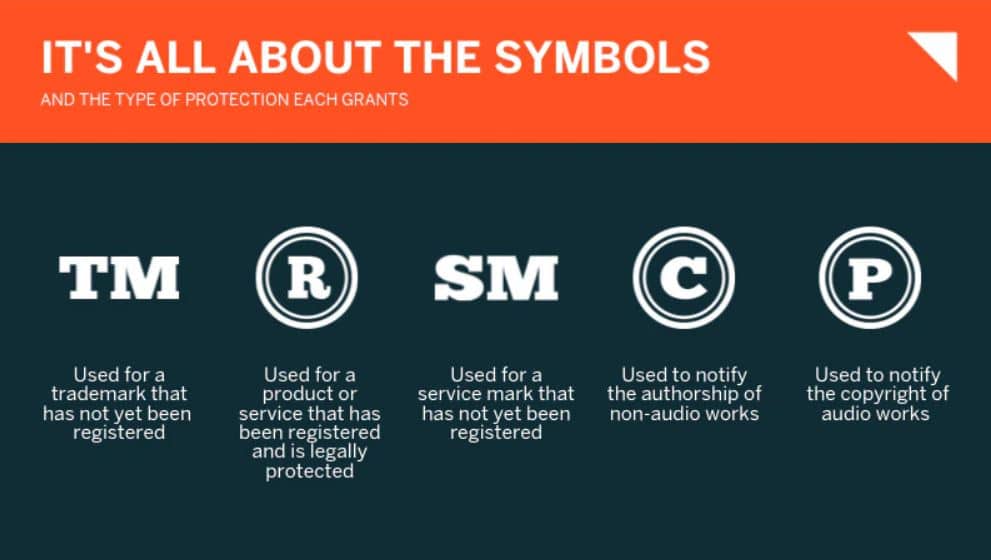
Trademark Symbols
Trade Mark (TM) and Service Mark (SM)
This symbolizes that the trademark has not yet been registered, but an application for the same is pending. It is put up to warn third parties lest they infringe upon the same. There is no specific legal significance as such because the application has not yet been approved by the authorities.
R Symbol
On the approval of the trademark application, you, as the proud owner of the newly registered trademark, are empowered to display the R symbol next to the trademark. This symbolizes that the trademark is officially registered, that infringement of any kind by a third party will be punishable by law.
It is not mandatory to display the R symbol. However, it protects the owner of the trademark in a way that, should anyone rip-off the actual product, on suing the third party for infringement, he has a right to recover all the profits that were lost. This is because the court requires the owner to prove that the infringer was aware of the fact that the trademark was registered and yet went ahead to use it without any prior permission.
C Symbol
The C symbol is generally used to signify copyright that the owner has over some creative work. This includes:
– Artwork- Photography
– Videography
– Literary Works
– Software
The C symbol is valid for a lifetime. The symbol is used with the copyright holder’s name and the year of the first publication in the country where the work was copyrighted. All in all, there is a lot that one must be aware of when it comes to trademarks and their registration. The process, in itself, is quite tricky, which is why the applicant must carry out proper research concerning the same. Therefore, registering your trademark has benefits aplenty provided it is done with due care.
9. Benefits of Trademark Registration in India
Trademark is a unique symbol or sign which may be a label or numeral or combination of colors for identification of your goods or services. You can obtain a trademark registration under the Trademarks Act, 1999.
Trademark enables you and a third party to distinguish your products and services from those belonging to your competitor. However, it would be helpful to keep in mind that geographical names, common names, common trade words and common abbreviation cannot be registered as a trademark.
Apart from being unique, a Trademark should be easy to use, make your products marketable and create brand recognition for your products. Trademark registration has several advantages and benefits to the owner:
Legal protection: Upon trademark registration, Trademarks are classified as intellectual property and are therefore protected from infringement. Trademark registration also confers an exclusive right to the use of the trademark in relation to the “Class” of goods or service it represents. Once you have filed the trademark application, the Symbol “TM” can be used with your products. The symbol “R” can be put into use only after you have obtained registration of your trademark. Further, you can use the ® symbol only for the goods and/or services listed in the registration certificate.In the case of unauthorized use of a registered trademark, you can seek relief for infringement in appropriate courts in the country.
Product differentiation: Trademark registrations are distinct to the goods or services they represent. Trademark will enable differentiation of your product as against the products of your competitors. Also, since trademark registration will be valid for the entire class of goods or services so represented, it will help in distinctly identifying your products. Customers uniquely identify products carrying different trademark, thus creating a customer base for your product.
Brand recognition: Customers associate a product’s performance, quality, features, and so on with the company making such products. They identify the product generally by the logo, which would be a registered trademark. Trademark registration facilitates brand recognition for your goods and services. It also creates goodwill associated with the brand. Thus, your brand is recognized as well as carries a market value over time. Brand recognition welcomes new customers while retaining loyal customers.
Creation of an asset: Trademark registration creates an asset for a business enterprise. Trademark is recognized as an intangible asset for accounting and income tax purposes. Trademarks are intellectual property and carry a value associated with the products they represent. Trademarks can be sold, franchised, assigned or commercially exploited in any other manner. You can recognize the value or cost associated with trademarks in the books of accounts, and also claim a deduction for depreciation and recognize income from the same.
Business valuation and goodwill: Trademarks registered and associated with your products enhance your overall business value, goodwill and net worth in the industry. Your trademark communicates your quality assurance, distinct features of your products and your organization’s mission. Trademarks contribute to the growth of your business. They help retain loyal customers and protect the goodwill of your business.
Trademark recognition: Trademark registered in India is valid for ten years from the date of filing of an application . However, the trademark can be further renewed. In a case where you want to use your trademark outside India or expand your business outside India, you need approval or trademark registration in the respective countries. In such cases, your trademark registration and business in India acts as a base to obtain registrations outside India.
Business expansion: A trademark establishes a connection between the customers and the products of an enterprise. With efficient or unique products, you can create a customer base. Your trademark helps you in retaining and expanding the customer base. Registration of your trademark confers exclusive rights of use for 10 years and protects your business revenues. Business enterprises can leverage the benefits of a customer base by introducing new products and expanding their business.
THE FOURTH SCHEDULE TO TRADE MARKS RULES, 2002
Classification of goods and services – Name of the classes
(Parts of an article or apparatus are, in general, classified with the actual article or apparatus, except where such parts constitute articles included in other classes).
Class 1. Chemical used in industry, science, photography, agriculture, horticulture and forestry; unprocessed artificial resins, unprocessed plastics; manures; fire extinguishing compositions; tempering and soldering preparations; chemical substances for preserving foodstuffs; tanning substances; adhesive used in industry
Class 2 . Paints, varnishes, lacquers; preservatives against rust and against deterioration of wood; colorants; mordents; raw natural resins; metals in foil and powder form for painters; decorators; printers and artists
Class 3 . Bleaching preparations and other substances for laundry use; cleaning; polishing; scouring and abrasive preparations; soaps; perfumery, essential oils, cosmetics, hair lotions, dentifrices
Class 4 . Industrial oils and greases; lubricants; dust absorbing, wetting and binding compositions; fuels(including motor spirit) and illuminants; candles, wicks
Class 5 . Pharmaceutical, veterinary and sanitary preparations; dietetic substances adapted for medical use, food for babies; plasters, materials for dressings; materials for stopping teeth, dental wax; disinfectants; preparation for destroying vermin; fungicides, herbicides
Class 6. Common metals and their alloys; metal building materials;
transportable buildings of metal; materials of metal for railway tracks; non-electric cables and wires of common metal; ironmongery, small items of metal hardware; pipes and tubes of metal; safes; goods of common metal not included in other classes; ores
Class 7 . Machines and machine tools; motors and engines (except for land vehicles); machine coupling and transmission components (except for land vehicles); agricultural implements other than hand-operated; incubators for eggs
Class 8 . Hand tools and implements (hand-operated); cutlery; side arms; razors
Class 9 . Scientific, nautical, surveying, electric, photographic, cinematographic, optical, weighing, measuring, signalling, checking (supervision), life saving and teaching apparatus and instruments; apparatus for recording, transmission or reproduction of sound or images; magnetic data carriers, recording discs; automatic vending machines and mechanisms for coin-operated apparatus; cash registers, calculating machines, data processing equipment and computers; fire extinguishing apparatus
Class 10 . Surgical, medical, dental and veterinary apparatus and instruments, artificial limbs, eyes and teeth; orthopaedic articles; suture materials
Class 11 . Apparatus for lighting, heating, steam generating, cooking, refrigerating, drying ventilating, water supply and sanitary purposes
Class 12 . Vehicles; apparatus for locomotion by land, air or water
Class 13 . Firearms; ammunition and projectiles; explosives; fire works
Class 14 . Precious metals and their alloys and goods in precious metals or coated therewith, not included in other classes; jewellery, precious stones; horological and other chronometric instruments
Class 15. Musical instruments
Class 16 . Paper, cardboard and goods made from these materials, not included in other classes; printed matter; bookbinding material; photographs; stationery; adhesives for stationery or household purposes; artists’ materials; paint brushes; typewriters and office requisites (except furniture); instructional and teaching material (except apparatus); plastic materials for packaging (not included in other classes); playing cards; printers’ type; printing blocks
Class 17 . Rubber, gutta percha, gum, asbestos, mica and goods made from these materials and not included in other classes; plastics in extruded form for use in manufacture; packing, stopping and insulating materials; flexible pipes, not of metal
Class 18 . Leather and imitations of leather, and goods made of these materials and not included in other classes; animal skins, hides, trunks and travelling bags; umbrellas, parasols and walking sticks; whips, harness and saddlery
Class 19 . Building materials, (non-metallic), non-metallic rigid pipes for building; asphalt, pitch and bitumen; non-metallic transportable buildings; monuments, not of metal.
Class 20 . Furniture, mirrors, picture frames; goods(not included in other classes) of wood, cork, reed, cane, wicker, horn, bone, ivory, whalebone, shell, amber, mother- of-pearl, meerschaum and substitutes for all these materials, or of plastics
Class 21 . Household or kitchen utensils and containers(not of precious metal or coated therewith); combs and sponges; brushes(except paints brushes); brush making materials; articles for cleaning purposes; steelwool; unworked or semi-worked glass (except glass used in building); glassware, porcelain and earthenware not included in other classes
Class 22 . Ropes, string, nets, tents, awnings, tarpaulins, sails, sacks and bags (not included in other classes) padding and stuffing materials(except of rubber or plastics); raw fibrous textile materials
Class 23 . Yarns and threads, for textile use
Class 24 . Textiles and textile goods, not included in other classes; bed and table covers.
Class 25 . Clothing, footwear, headgear
Class 26 . Lace and embroidery, ribbons and braid; buttons, hooks and eyes, pins and needles; artificial flowers
Class 27 . Carpets, rugs, mats and matting, linoleum and other materials for covering existing floors; wall hangings(non-textile)
Class 28 . Games and playthings, gymnastic and sporting articles not included in other classes; decorations for Christmas trees
Class 29 . Meat, fish, poultry and game; meat extracts; preserved, dried and cooked fruits and vegetables; jellies, jams, fruit sauces; eggs, milk and milk products; edible oils and fats
Class 30 . Coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar, rice, tapioca, sago, artificial coffee; flour and preparations made from cereals, bread, pastry and confectionery, ices; honey, treacle; yeast, baking powder; salt, mustard; vinegar, sauces, (condiments); spices; ice
Class 31. Agricultural, horticultural and forestry products and grains not included in other classes; live animals; fresh fruits and vegetables; seeds, natural plants and flowers; foodstuffs for animals, malt
Class 32 . Beers, mineral and aerated waters, and other non-alcoholic drinks; fruit drinks and fruit juices; syrups and other preparations for making beverages
Class 33 .Alcoholic beverages(except beers)
Class 34 . Tobacco, smokers’ articles, matches
SERVICES
Class 35 .Advertising, business management, business administration, office functions.
Class 36 .Insurance, financial affairs; monetary affairs; real estate affairs.
Class 37 . Building construction; repair; installation services.
Class 38. Telecommunications.
Class 39. Transport; packaging and storage of goods; travel arrangement.
Class 40. Treatment of materials.
Class 41. Education; providing of training; entertainment; sporting and cultural activities.
Class 42. Scientific and technological services and research and design relating thereto; industrial analysis and research services; design and development of computer hardware and software.
Class 43. Services for providing food and drink; temporary accommodation.
Class 44. Medical services, veterinary services, hygienic and beauty care for human beings or animals; agriculture, horticulture and forestry services.
Class 45. Legal services; security services for the protection of property and individuals; personal and social services rendered by others to meet the needs of individuals.
https://ipindiaonline.gov.in/tmrpublicsearch/frmmain.aspx – Search your name for the application.